The Repo Rate is a key tool used by central banks to manage the economy and ensure stability. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of the repo rate, its significance in monetary policy, and its impact on various economic factors.
How Repo Rate Works
The role of the central bank: The central bank sets the repo rate, which is the rate at which it lends money to commercial banks. This rate serves as a benchmark for short-term borrowing in the financial markets.
Relationship between central bank and commercial banks: Commercial banks borrow funds from the central bank at the repo rate to meet their short-term liquidity requirements. By adjusting the repo rate, the central bank can influence the cost of borrowing for banks and, in turn, influence economic activity.
Impact on the overall economy: Changes in the repo rate have a ripple effect on the economy. A reduction in the repo rate encourages borrowing and spending, stimulating economic growth. On the other hand, an increase in the repo rate can curb inflationary pressures and prevent the economy from overheating.
Factors Influencing Repo Rate
Inflation rate: Maintaining price stability is a key objective of monetary policy. The central bank adjusts the repo rate in response to changes in inflation to ensure that prices remain stable and inflation is kept in check.

Image courtesy of www.tbsnews.net via Google Images
Economic growth: The repo rate also plays a crucial role in supporting economic growth. By lowering the repo rate, the central bank can make borrowing cheaper, encouraging investment and consumption, which can boost overall economic activity.
Money supply in the economy: The repo rate affects the money supply in the economy. By adjusting the repo rate, the central bank can influence liquidity conditions, impacting credit availability and spending patterns in the economy.
Importance of Repo Rate in Monetary Policy
Controlling inflation: One of the primary objectives of monetary policy is to maintain price stability. By adjusting the repo rate, the central bank can control inflationary pressures and ensure that prices remain stable over the long term.
Stimulating economic growth: Lowering the repo rate can stimulate economic growth by making borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers. This can lead to increased investment, consumption, and overall economic activity.
Regulating money supply: The repo rate plays a vital role in regulating the money supply in the economy. By adjusting the repo rate, the central bank can influence credit creation and spending patterns, helping to maintain financial stability.
Effects of Repo Rate Changes
Impact on interest rates: Changes in the repo rate have a direct impact on interest rates in the economy. A decrease in the repo rate typically leads to lower interest rates on loans and savings, making borrowing more affordable for businesses and consumers.
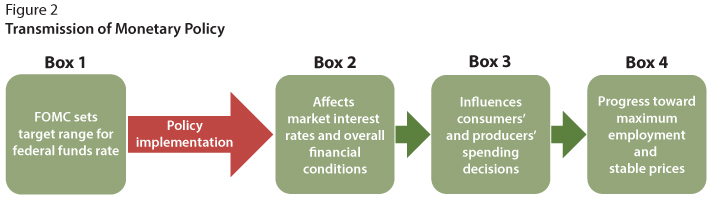
Image courtesy of research.stlouisfed.org via Google Images
Influence on borrowing and lending behaviors: Changes in the repo rate can influence borrowing and lending behaviors in the economy. Lowering the repo rate can incentivize borrowing and spending, while raising the repo rate can encourage saving and curb excessive borrowing.
Implications for consumers and businesses: Consumers and businesses are directly affected by changes in the repo rate. Lower repo rates can lead to cheaper loans, making it easier for individuals to finance purchases and for businesses to invest in growth opportunities.
Current Repo Rate Trends
Overview of repo rates in different countries: Repo rates vary across countries based on their economic conditions and policy objectives. Central banks worldwide use the repo rate as a tool to manage monetary policy and support economic stability.
Recent changes in repo rates: In response to economic conditions, central banks may adjust the repo rate to achieve their policy goals. Recent changes in repo rates reflect the central bank’s stance on inflation, economic growth, and financial stability.
Future outlook for repo rates: The future trajectory of repo rates depends on a variety of factors, including inflation trends, economic growth projections, and global market conditions. Central banks carefully consider these factors when setting repo rate policies.
Conclusion
The repo rate is a critical tool in monetary policy that influences borrowing costs, economic growth, and inflation. Understanding the repo rate is essential for making informed financial decisions and navigating the complexities of the economy.
To stay abreast of economic developments and policy changes, individuals and businesses should monitor repo rate announcements, central bank communications, and economic indicators that influence repo rate decisions.
By understanding the repo rate and its implications, individuals can make sound financial decisions, such as borrowing at the right time, investing wisely, and planning for economic uncertainties.



