Welcome to our comprehensive guide on understanding put options! Whether you are an experienced investor or just starting your journey in the world of options trading, this blog will provide you with the knowledge and insights needed to unlock the power of put options. In this guide, we will cover everything from the basics of put options to advanced trading strategies and risk management techniques. So let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries of put options!
What are Put Options?
Before we delve into the mechanics of put options, it’s important to understand what they are and how they differ from call options. Put options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specific asset (usually stocks) at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, on or before the expiration date.
Put options are often used as a form of insurance against potential price declines in the underlying asset. As the stock price decreases, the value of the put option increases, allowing the holder to sell the asset at a higher price than the market value.
The Mechanics of Put Options
Put options have several key components that determine their value and behavior:
Strike Price and Expiration Date
The strike price is the price at which the put option holder can sell the underlying asset. The expiration date is the deadline by which the put option must be exercised. It’s important to note that put options have a finite lifespan and become worthless if not exercised before expiration.
Intrinsic Value vs. Extrinsic Value
The intrinsic value of a put option is the difference between the strike price and the current market price of the underlying asset. If the asset’s market price is below the strike price, the put option has intrinsic value. Extrinsic value, also known as time value, is influenced by factors such as time remaining until expiration, market volatility, and interest rates.
Factors Influencing the Value of Put Options
Several factors can impact the value of a put option:
- Price movements of the underlying asset
- Volatility in the market
- Time remaining until expiration
- Interest rates
Understanding these factors can help investors make informed decisions about buying, selling, or holding put options.
Understanding Options Trading Strategies
Now that we’ve covered the basics of put options, let’s explore some popular trading strategies:
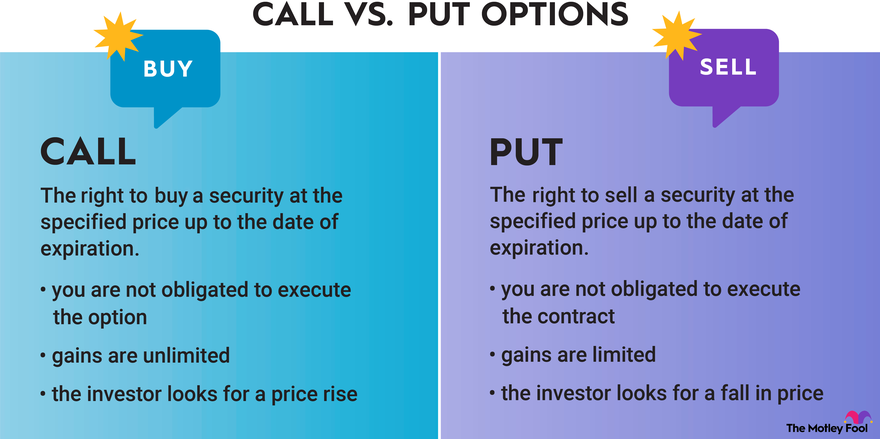
Image courtesy of www.fool.com via Google Images
Hedging Strategies Using Put Options
One of the primary purposes of put options is to hedge against potential losses in an investment portfolio. By purchasing put options on assets held in the portfolio, investors can protect themselves from potential downside risks. If the market experiences a decline, the put options will increase in value, offsetting some of the losses.
Hedging with put options is especially useful for investors holding stocks that they believe may face a downturn. By purchasing put options on these stocks, investors have the right to sell them at a predetermined price, providing a safety net in case the prices plummet.
Speculative Strategies with Put Options
Put options can also be used speculatively to profit from anticipated price declines. Investors who expect a particular stock or market to decline in value can buy put options with a strike price below the current market price. If their predictions are correct, the put options will increase in value, allowing them to sell the asset at a higher price than its market value.
Furthermore, more advanced trading strategies, such as option spreads and combinations, allow investors to create complex positions using multiple put options to capitalize on specific market scenarios. These strategies often involve a combination of buying and selling put options at different strike prices and expiration dates.
Key Terminology and Concepts Associated with Put Options
When dealing with put options, understanding key terminology and concepts is essential for making informed decisions:
Delta, Gamma, and Theta: Greeks of Put Options
- Delta measures the rate at which the price of an option changes relative to the price movement of the underlying asset. A delta of -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation between the option and the underlying asset.
- Gamma measures the rate of change in the delta of an option in response to changes in the price of the underlying asset.
- Theta represents the time decay of an option’s value. As expiration approaches, all other factors remaining constant, the value of the option decreases.
Implied Volatility and Its Impact on Put Option Pricing
Implied volatility refers to the market’s expectations of future volatility in the underlying asset. High implied volatility leads to increased option prices due to the higher likelihood of significant price fluctuations. Investors must take into account implied volatility when analyzing the pricing and potential profitability of put options.
Option Spreads and Combinations
Option spreads and combinations involve using multiple put options with different strike prices and expiration dates to create complex positions. These strategies aim to minimize risk and maximize potential profits by combining various options to suit specific market conditions and investor objectives.
Evaluating the Risk-Reward Tradeoff of Put Options
While put options offer several advantages, it’s crucial to consider the risk-reward tradeoff involved:
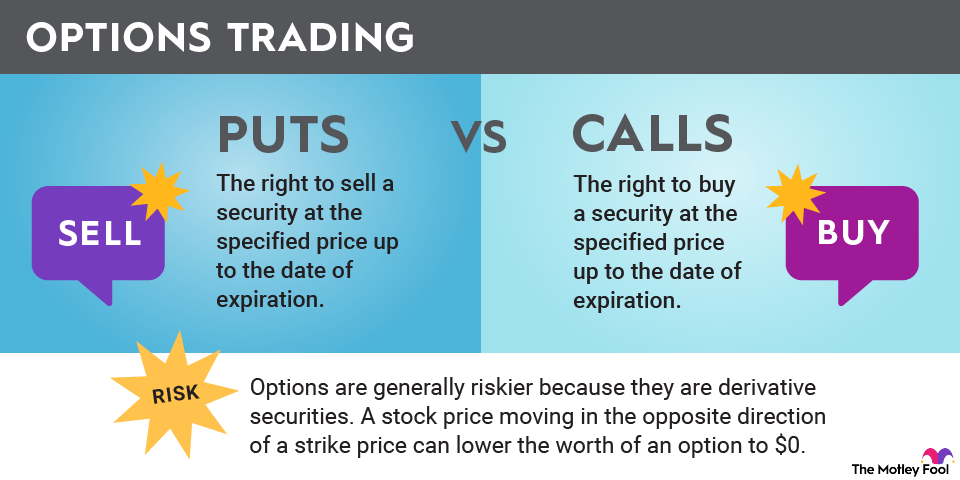
Image courtesy of www.fool.com via Google Images
Advantages of Using Put Options
1. Protection against downside risks: Put options act as insurance, allowing investors to protect their portfolios from potential losses during market downturns. If correctly implemented, put options can act as a safety net, limiting losses in a declining market.
2. Versatility in trading strategies: Put options offer flexibility and can be used in a variety of hedging and speculative trading strategies. Investors can tailor their option positions to their specific risk appetite, objectives, and market outlook.
Limitations and Risks of Put Options
1. Time decay and limited lifespan: Put options have an expiration date, after which they become worthless if not exercised. As time passes, the value of the option erodes due to time decay, putting pressure on investors to make timely and accurate predictions.
2. Potential for loss of entire premium: If the price of the underlying asset remains above the strike price, put options may expire worthless, resulting in a loss of the premium paid to acquire them.
Real-World Examples of Put Options in Action
To understand the practical application of put options, let’s examine some real-world scenarios:
Case Study: The “Black Swan” Event and Protective Put Options
During the 2008 financial crisis, many investors suffered significant losses as stock markets plummeted. However, those who had purchased put options to protect their portfolios were able to limit their losses by selling the assets at higher prices than the market value.
Put Options as a Risk Management Tool in Volatile Industries
Industries like oil and gas, technology, and biotech are known for their volatility. Investors in these sectors often use put options to protect their positions from sudden market shifts or adverse events that can have a significant impact on stock prices.
Successful Investment Stories Utilizing Put Options
Many successful investors and traders have achieved substantial profits through the strategic use of put options. Warren Buffett’s famous bet against the housing market before the 2008 financial crisis is just one example of how put options can generate significant returns when correctly utilized.
Tips for Safeguarding Investments with Put Options
To effectively incorporate put options into your investment strategy, consider implementing the following tips:

Image courtesy of www.fool.com via Google Images
Proper Risk Assessment and Diversification
Before purchasing put options, conduct thorough research and assess the potential risks and rewards. Diversify your options portfolio to mitigate risk and avoid overexposure to specific assets or industries.
Regular Monitoring of Option Positions
Stay vigilant and keep a close eye on the market and your options positions. Monitor changes in the value of your put options, market conditions, and any relevant news or events that may impact the underlying assets.
Staying Abreast of Market News and Events
To make informed decisions about buying or selling put options, stay up to date with the latest market news and developments. Stay informed about industry trends, company announcements, and economic indicators that can influence the value of the underlying assets.
Conclusion
Put options can be powerful tools in an investor’s arsenal, providing risk management, hedging, and speculative opportunities. By understanding the mechanics of put options, implementing sound trading strategies, and managing associated risks, investors can effectively incorporate these financial instruments into their investment toolkit. Remember, education and thorough research are key to successful options trading. So, take the time to learn and practice before venturing into the world of put options, and always remember to consult with a financial advisor or professional when making investment decisions.
With the knowledge gained from this guide, you are now equipped to unlock the potential of put options. So go forth, explore, and may your investments prosper!



