Brief overview of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and its mission to promote cooperation among central banks and enhance global financial stability.
History of the BIS
The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) was established in 1930 to facilitate reparations payments after World War I. Over the years, it evolved into a key player in international monetary policy and financial regulation.
Structure and Functions of the BIS
The BIS is owned by 63 member central banks around the world and serves as a forum for policy discussions. Its key functions include conducting research on financial trends and providing banking services to central banks.
Impact of the BIS on Global Financial Stability
The BIS plays a crucial role in promoting cooperation among central banks to address financial crises and economic challenges. It has influenced regulatory frameworks and monetary policy decisions at the global level, contributing to stability.
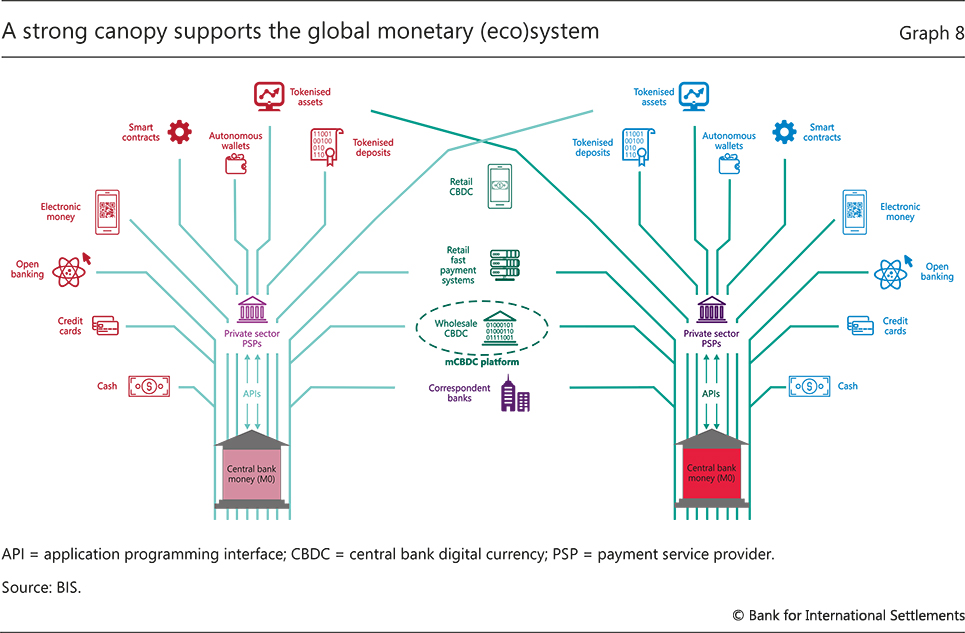
Image courtesy of www.bis.org via Google Images
Criticisms and Challenges Facing the BIS
Despite its important role, the BIS has faced criticism for being too secretive and lacking accountability. It also confronts challenges in a rapidly changing financial landscape, such as the emergence of digital currencies and geopolitical tensions.
And So
The Bank for International Settlements is a vital institution for maintaining stability and resilience in the global financial system. Its role in fostering international monetary and financial cooperation is essential for addressing current and future challenges.



